

Get paystubs when you need them, without the wait. Our paystub generator uses the same industry-leading tax software trusted by top payroll providers, ensuring accurate and professional documents every time.
Create Your Paystub Now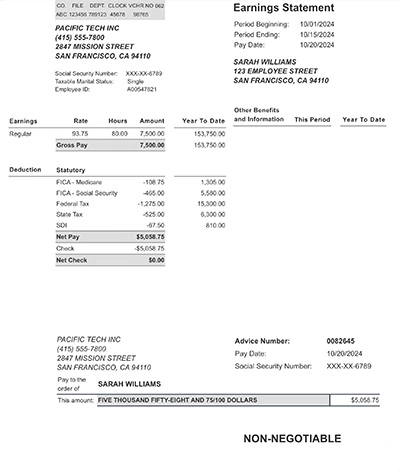
Creating your pay stub is simple with our online generator. Input your information, make any adjustments, and let our system generate your documents instantly.
Our intuitive form makes creating professional paystubs effortless and accurate. Simply enter your employer details, earnings information, and tax deductions while our smart system guides you through each step to ensure nothing is missed.
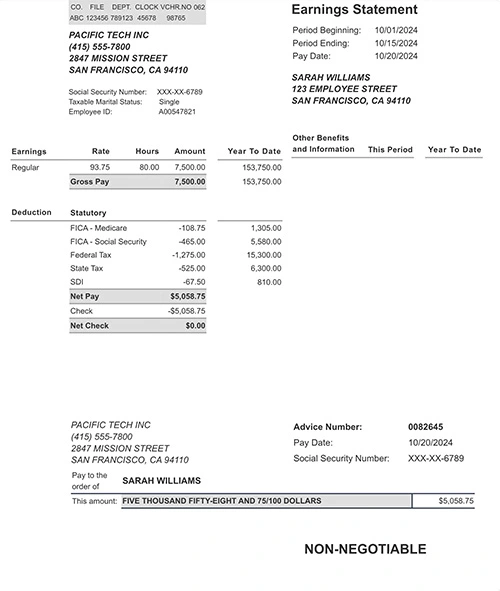
Take a moment to review your perfectly formatted check stub before finalizing. Our preview system lets you examine every detail, from tax calculations to year-to-date totals, ensuring your paystub meets your exact needs.
The moment you're satisfied with your preview, your professional pay stub is ready for immediate delivery. Download your PDF instantly or receive it directly in your email inbox - your choice of delivery makes accessing your paystub convenient and quick.
See why thousands of users trust PayStubsNow's paystub generator to create accurate, professional pay stubs instantly for income verification and payroll documentation.
Generate pay stubs in minutes
Choose from a variety of professionally designed paystub templates
Make accurate paystubs with automated tax computing
Generate confidential documents safely
Say goodbye to tedious calculations and paperwork. Our tool automates the process to reduce mistakes and free up your time for what matters most—growing your business or enjoying your day.
Provide clear, detailed paystubs that help employees understand their earnings, deductions, and taxes. Make payroll information accessible and straightforward to build trust and open communication channels.
Keep all your payroll records in one secure place. Our generator helps you manage payments efficiently, which makes it simple to access past stubs and monitor financial transactions over time.
With PayStubsNow, you can create professional pay stubs without having to wait. Our templates ensure your documents meet professional standards, reflect your business well, and satisfy any formal requirements. There are no complicated steps—just quick, accurate paystub generation.
PayStubsNow offers payroll solutions that fit your budget. You can make pay and check stubs anytime, knowing your information stays secure. Affordable and easy to use—handling payroll just got simpler.
Use PayStubsNow to ensure your paystubs are accurate and comply with current tax and employment laws. You don't have to worry about legal details—our paystub generator takes care of them so that you can focus on other tasks.
Choose from our variety of professional paystub layouts designed for different industries and purposes. Our check stub generator offers flexible options to create the exact documentation you need, whether for income verification, loan applications, or employee records—all while maintaining consistent accuracy and professionalism.
Create professional pay stubs in just minutes with our straightforward three-step process. Enter your information, preview your perfectly formatted check stub, and download your completed document instantly. Our paystub generator handles complex calculations while keeping the experience simple and efficient.